STUDY DESIGN
Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Study
Author Information School of Kinesiology, Molecular and Applied Sciences Laboratory, Auburn University, AL.
Kephart WC, Wachs TD, Mac Thompson, Brooks Mobley, Fox CD, McDonald JR, Ferguson BS, Young KC, Nie B, Martin JS, Pascoe DD, Arnold RD, Moon JR, Roberts MD
BACKGROUND
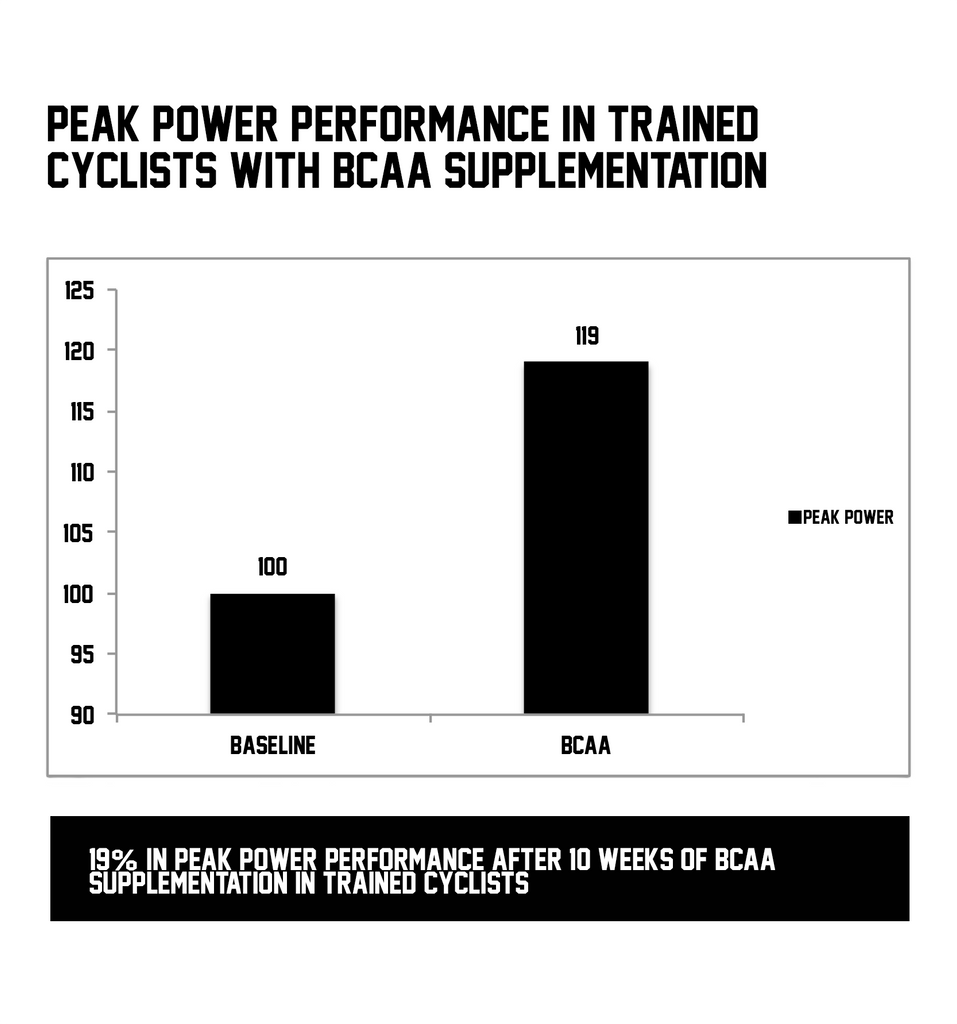
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of BCAA supplementation with trained cyclists on select body composition, performance, and/or immune variables over a 10-week training season.
METHODS
18 trained cyclists were administered 12g of BCAA (6 g/day L-Leucine, 2 g/day L-Isoleucine and 4 g/day L-Valine) of either branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs, n = 9) or a maltodextrin placebo (PLA, n = 9) over a 10-week training season. Before and after the 10-week study, the following was assessed: (1) 4-h fasting blood draws; (2) dual X-ray absorptiometry body composition; (3) Wingate peak power tests; and (4) 4 km time-trials. No group × time interactions existed for total lean mass (P = 0.27) or dual-leg lean mass (P = 0.96).
RESULTS
A significant interaction existed for body mass-normalized relative peak power (19 % increase in the BCAA group pre-to post-study, P = 0.01), and relative mean power (4 % increase in the BCAA group pre- to post-study, P = 0.01). A significant interaction for neutrophil number existed (P = 0.04), as there was a significant 18 % increase within the PLA group from the pre-to post-study time point (P = 0.01). BCAA supplementation improves sprint performance variables in endurance cyclists. Additionally, given that BCAA supplementation blunted the neutrophil response to intense cycling training, BCAAs may benefit immune function during a prolonged cycling season.
Adapted from The Journal Of Amino Acids
DOWNLOAD THE CLINICAL STUDY BELOW













