Study Design: Randomized Controlled Trial (RCT)
Author Information
- QiQi Zhou1,2,
- Meghan L Verne3,
- Jeremy Z Fields1,
- John J Lefante4,
- Sarpreet Basra1,
- Habeeb Salameh5,
- G Nicholas Verne1
Background
There is ample evidence from numerous clinical studies, that supports the use of L-glutamine as a dietary supplement to help maintain gut barrier function and strengthening lining, to reduce intestinal permeability and help potentially treat Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS).
More effective treatments are needed for patients with postinfectious, diarrhea-predominant, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D). Accordingly, this study conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 8-week-long trial to assess the efficacy and safety of oral glutamine therapy in patients who developed IBS-D with increased intestinal permeability following an enteric infection.
Methods
Eligible adults were randomized into a glutamine group and administered 15g per day or active placebo (whey protein) group for 8 weeks. The primary goal was a reduction of 50 or more points on the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Severity Scoring System (IBS-SS). Secondary goals included: raw IBS-SS scores, changes in daily bowel movement frequency, stool form (Bristol Stool Scale) and intestinal permeability.
106 of the 115 test subjects were randomly assigned to two groups: Glutamine group (n = 54) receiving 15g of Glutamine per day and the placebo group (n = 52) receiving a placebo, which consisted of 15g of Whey Protein for 8 weeks.
Results
The results were staggering and showed
80% of Glutamine patients achieved their primary goal with a reduction of 50 or more points on the Irritable Bowel Syndrome Severity Scoring System
Glutamine also significantly reduced daily bowel movement frequency (3 vs. 5)
Stool Form Measured on the Bristol Stool Scale Scores were reduced from (4 vs. 6.5)
Intestinal permeability was also completely normalized in the Glutamine group, but not the control group
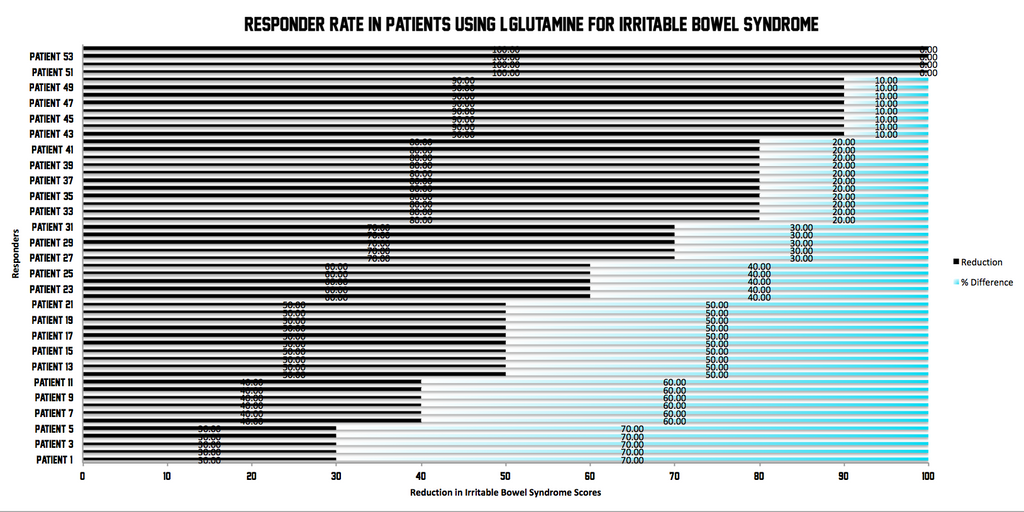
Conclusions
In patients with IBS-D with intestinal hyperpermeability following an enteric infection, oral dietary glutamine supplements dramatically and safely reduced all major IBS-related endpoints. This study shows that L-Glutamine supplementation can effectively treat and reduce symptoms of IBS such as intestinal permeability, bowel movement frequency, bowel quality and overall quality of life factors.














