Effects of Beta-Alanine Supplementation And High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) On Endurance Performance And Body Composition And Men
Study Design: Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial
Author Information
Abbie E Smith,1 Ashley A Walter,2 Jennifer L Graef,1 Kristina L Kendall,1 Jordan R Moon,1Christopher M Lockwood,1 David H Fukuda,1 Travis W Beck,2 Joel T Cramer,2 and Jeffrey R Stout
Metabolic and Body Composition Laboratory, Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK 73019, USA
Biophysics Laboratory; Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK 73019, USA
Background
Intermittent bouts of high-intensity exercise result in diminished stores of energy substrates, followed by an accumulation of metabolites, promoting chronic physiological adaptations. In addition, beta-alanine has been accepted has an effective physiological hydrogen ion (H+) buffer. Concurrent high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and beta-alanine supplementation may result in greater adaptations than HIIT alone. The purpose of the current study was to evaluate the effects of combining beta-alanine supplementation with high-intensity interval training (HIIT) on endurance performance and aerobic metabolism in recreationally active college-aged men.
Methods
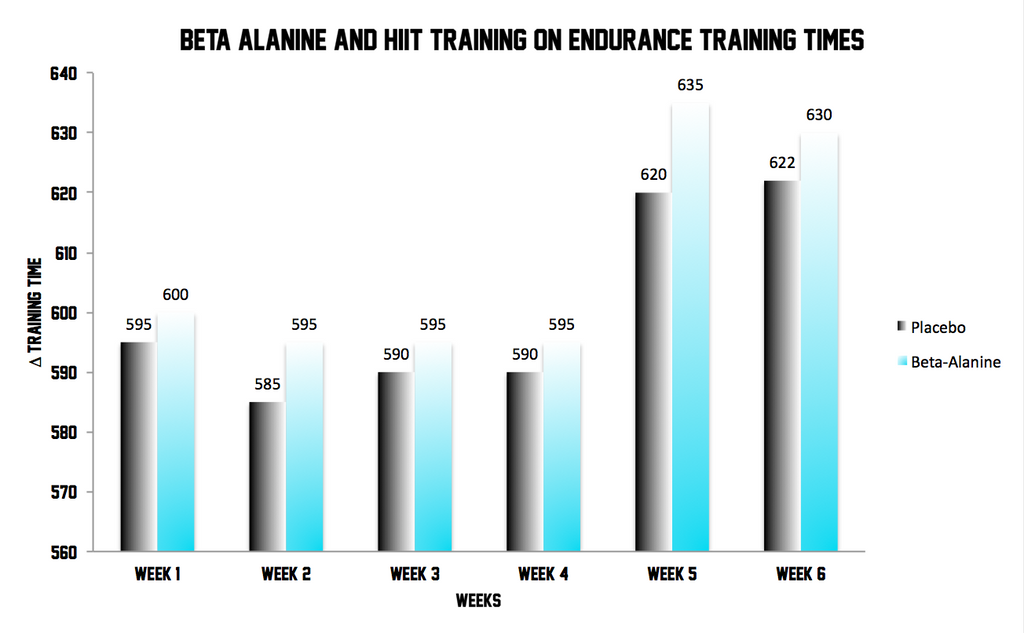
Forty-six men (Age: 22.2 ± 2.7 yrs; Ht: 178.1 ± 7.4 cm; Wt: 78.7 ± 11.9; VO2peak: 3.3 ± 0.59 l·min-1) were assessed for peak O2 utilization (VO2peak), time to fatigue (VO2TTE), ventilatory threshold (VT), and total work done at 110% of pre-training VO2peak (TWD). In a double-blind fashion, all subjects were randomly assigned into one either a placebo (PL – 16.5 g dextrose powder per packet; n = 18) or β-alanine (BA – 1.5 g β-alanine plus 15 g dextrose powder per packet; n = 18) group. All subjects supplemented four times per day (total of 6 g/day) for the first 21-days, followed by two times per day (3 g/day) for the subsequent 21 days, and engaged in a total of six weeks of HIIT training consisting of 5–6 bouts of a 2:1 minute cycling work to rest ratio.
Results
Significant improvements in VO2peak, VO2TTE, and TWD after three weeks of training were displayed (p < 0.05). Increases in VO2peak, VO2TTE, TWD and lean body mass were only significant for the BA group after the second three weeks of training.
Conclusions
The use of HIIT to induce significant aerobic improvements is effective and efficient. Chronic beta-alanine supplementation may further enhance HIIT, improving endurance performance and lean body mass.