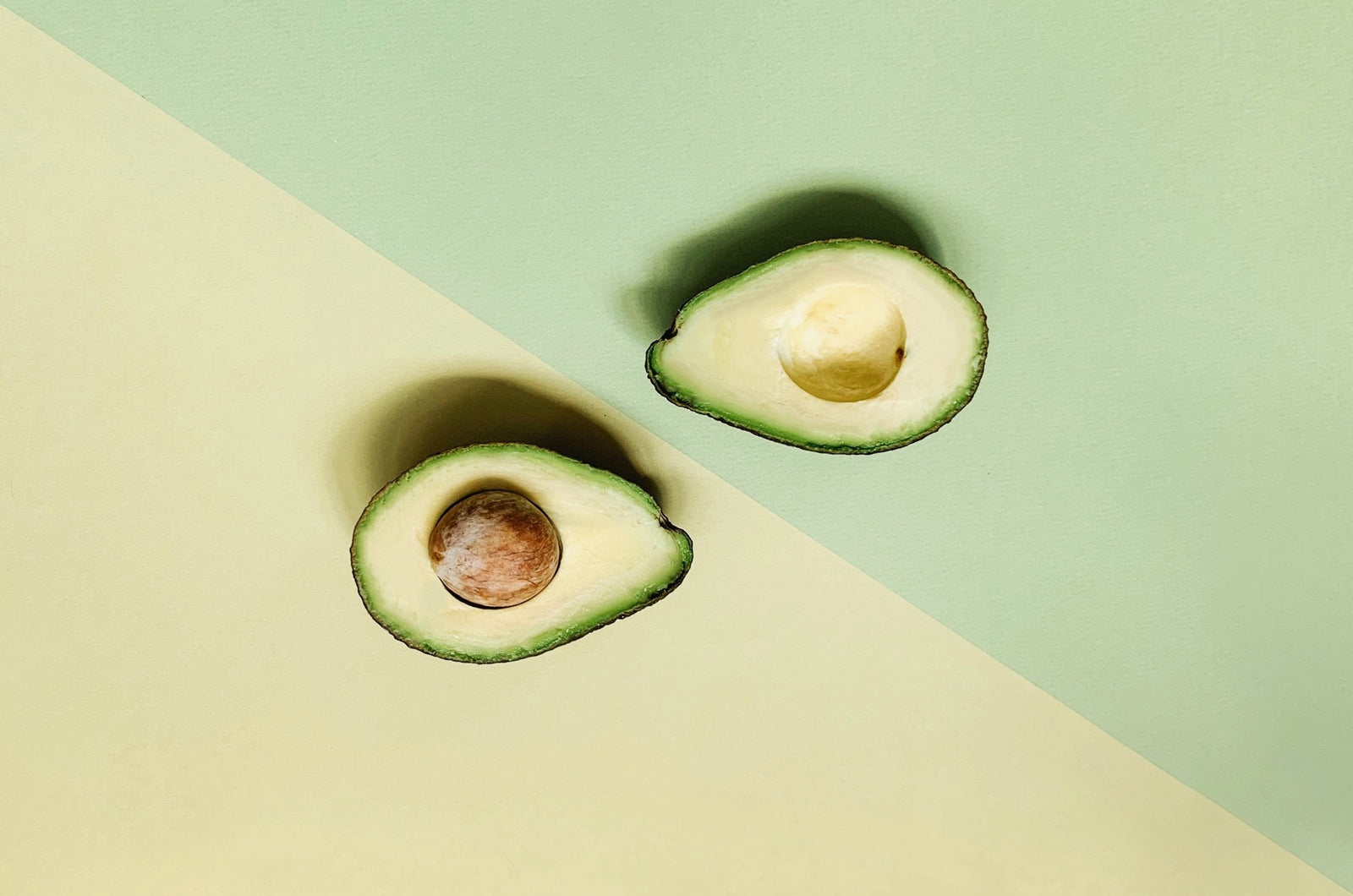
Avocado Nutrition
You’ll never believe this, but avocados are a fruit. Avocados are nutrient dense and great sources of vitamin C, E, K, folate and potassium, and perhaps most well known for their healthy omega-3 fatty acids which have been shown to benefit and improve cognitive function, mood, reduce the risk for heart disease, and joints.
Roughly one serving of avocado 100g (or half an avocado) contains
Calories: 160
Fat: 14.7g – (10g of monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA) and 2 g polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA), with the predominant fatty acid being oleic acid at 11.06 g/serving )
Carbohydrates: 8.5g
Fiber: 6.7g
Sugar: Less than 1g
Potassium: 500mg
Vitamin K: 20% DV
Folate: 20% DV
Pantothenic Acid: 30% DV
Copper: 20% DV
5 Avocado Nutritional Benefits And Why You Need Them In Your Diet
1. Avocados Improve Cholesterol Levels And Lipid Profiles
Avocados are high in fat, but it’s not what you think. Avocados have the type of fat you want in a healthy well-balanced diet. Avocados contain roughly 20-25g of fat per fruit, most of it in the form of healthy omega-3 monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats.
A meta-analysis, assessing avocado intake and plasma lipoproteins, found that avocado intake was associated with reduced total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and triglycerides while increasing high-density lipoproteins (HPL-C), otherwise known as good cholesterol. When you have too much cholesterol in your blood, it builds up in the walls of your arteries, causing a process called atherosclerosis, a form of heart disease. The arteries become narrowed and blood flow to the heart muscle is slowed down or blocked. Therefore, the potassium found in avocados can help in preventing too much bad cholesterol from forming by stabilizing your heartbeat, and promoting better vascular health keeping your arteries free and clear of plaque buildup.
2. Avocados Help You Absorb Nutrients
One of the most impressive nutritional benefits of avocados is that they are associated with increased and optimal nutrient uptake. Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) revealed that avocado consumption was associated with better diet quality, including significantly higher intake of fruits, vegetables, and a lower intake of added sugars. Those who eat avocados also had significantly higher intakes of dietary fiber, vitamins E and K, magnesium, and potassium by eating half an avocado per day.
Research has shown that avocados can increase the absorption of lipid-soluble bioactive phytonutrients such as carotenoids. Adding avocado to salsa for example, enhances the absorption of lycopene and β-carotene, while adding avocado to a salad increases absorption of α-carotene, β-carotene, and lutein. Including avocado in your nutrition plan with other foods, increases the absorption of β-carotene and increasing the conversion of β-carotene to vitamin A 13-fold. Better nutrient uptake of course, will help with total body and biological function.
3. Avocados May Help Your Vision
Avocado consumption enhances the absorption of the carotenoids lutein and zeaxanthin, which accumulate in the eyes and brain. Lutein helps minimize UV damage from sunlight. Avocados also help with the absorption of other beneficial fat soluble vitamins, beta-carotene which also contribute to eye health reducing the risk for potential age related degenerative disease.
4. Avocados Aid In Weight Loss
Rising obesity rates have made weight loss a common goal shared amongst the general population. Creating a well-rounded and healthy nutrition plan with foods such as avocados, can help aid in weight loss, by increasing satiety and reducing hunger when included with meals. Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) shows that people who eat avocados are 33% less likely to be overweight or obese and 32% less likely to have an elevated waist circumference compared to non-consumers, with total lower body weight, BMI, and better body composition. Despite the higher amount of fat content, studies show that there are avocado weight loss benefits. That means you can eat a whole avocado per day, without derailing your weight loss efforts [R].
5. Avocados Have A Ton Of Fiber
Your body needs ample amounts of insoluble and soluble fiber, for optimal digestive and gut health. In one whole avocado, you get nearly 50% of your daily fiber needs. The fiber from avocados will benefit and nourish a healthy gut microbiome, and help your intestinal tract run smoothly.
Avocado Nutritional Benefits: Takeaway
Besides being delicious, smooth, and creamy, the benefits of avocados, go beyond the mouthwatering guacamole you’ve grown to love. Avocado's nutritional benefits include supporting your heart health by stabilizing cholesterol levels, improving your digestive health, helping you absorb your nutrients, and even aiding in weight loss. There’s no reason why you shouldn’t include these nutrient-rich, creamy delights in your diet, when there are so many health benefits. If you don’t like avos, then throw in half into a green smoothie for a creamier, and richer texture. It will take your smoothie game from good to great, and you won’t even taste it.
Need Help With Optimizing Your Diet And Nutrition Plan To Finally Get The Results You've Been Waiting For?
SWOLVERINE IS AN ENDURANCE ATHLETE AND ACTIVE LIFESTYLE BRAND. MADE FOR THE ELITE ATHLETE, AND THE STRONG-WILLED OUR PRODUCTS WERE DESIGNED TO FUEL YOUR ATHLETIC PERFORMANCE. WE PERFORM WHEN YOU PERFORM.
We believe that everyone can optimize not only their athletic performance but their human potential. The way we believe we can optimize performance is through transparency, clinically effective doses, and clinically proven ingredients with evidence-based outcomes. We provide the nutrients you need to power your active lifestyle.
References
Impact of avocado-enriched diets on plasma lipoproteins: A meta-analysis. Peou S, Milliard-Hasting B, Shah SA J Clin Lipidol. 2016 Jan-Feb; 10(1):161-71. [PubMed] [Ref list]
Avocado consumption is associated with better diet quality and nutrient intake, and lower metabolic syndrome risk in US adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001-2008. Fulgoni VL 3rd, Dreher M, Davenport AJ Nutr J. 2013 Jan 2; 12():1. [PubMed] [Ref list]
Carotenoid absorption from salad and salsa by humans is enhanced by the addition of avocado or avocado oil.Unlu NZ, Bohn T, Clinton SK, Schwartz SJ J Nutr. 2005 Mar; 135(3):431-6. [PubMed] [Ref list]
Avocado consumption enhances human postprandial provitamin A absorption and conversion from a novel high-β-carotene tomato sauce and from carrots.Kopec RE, Cooperstone JL, Schweiggert RM, Young GS, Harrison EH, Francis DM, Clinton SK, Schwartz SJ J Nutr. 2014 Aug; 144(8):1158-66. [PubMed] [Ref list]
O'Neil CE, Nicklas TA, Fulgoni VL., 3rd Avocado consumption by adults is associated with better nutrient intake, diet quality, and some measures of adiposity: National health and nutrition examination survey, 2001-2012. Int Med Rev. (2017). 3:422 10.18103/imr.v3i4.422 [CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [Ref list]
Avocado consumption is associated with better diet quality and nutrient intake, and lower metabolic syndrome risk in US adults: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001-2008.Fulgoni VL 3rd, Dreher M, Davenport AJNutr J. 2013 Jan 2; 12():1.[PubMed] [Ref list]
Hass Avocado Inclusion in a Weight-Loss Diet Supported Weight Loss and Altered Gut Microbiota: A 12-Week Randomized, Parallel-Controlled Trial. Henning SM, Yang J, Woo SL, Lee RP, Huang J, Rasmusen A, Carpenter CL, Thames G, Gilbuena I, Tseng CH, Heber D, Li Z Curr Dev Nutr. 2019 Aug; 3(8):nzz068.[PubMed] [Ref list]
Ford, Nikki A, and Ann G Liu. “The Forgotten Fruit: A Case for Consuming Avocado Within the Traditional Mediterranean Diet.” Frontiers in nutrition vol. 7 78. 29 May. 2020, doi:10.3389/fnut.2020.00078 [PubMed]
Find similar articles:
Nutrition