Study Design
Randomized Controlled Trial
Author Information
T Saunders B1, DE Salles Painelli V, DE Oliveira LF, DA Eira Silva V, DA Silva RP, Riani L, Franchi M, Gonçalves LS, Harris RC, Roschel H, Artioli GG, Sale C, Gualano B.
Applied Physiology and Nutrition Research Group, University of São Paulo, Brazil.
Musculoskeletal Physiology Research Group, Sport, Health and Performance Enhancement Research Centre, Nottingham Trent University, Nottingham, United Kingdom. Journal of Medical & Science In Sports & Exercise
Background
Introducing Beta-Alanine into the bloodstream raises carnosine levels, which helps counteract the development of lactic acid, created from the buildup of hydrogen ions. Lactic acid produces a burning sensation and causes increased fatigue, resulting in a loss of power and eventually fatigued muscles. Training at a higher-volume due to delayed muscle fatigue will increase output, which translates into increased strength and athletic performance. Skeletal muscle carnosine content can be increased through Beta-Alanine (BA) supplementation, but the maximum increase achievable with supplementation is unknown. No study has investigated the effects of prolonged supplementation on carnosine-related genes or exercise capacity. This study aimed to investigate the effects of 24 weeks of Beta-Alanine supplementation on muscle carnosine content, gene expression, and high-intensity cycling capacity CCT110%.
Methods
Twenty-five active males were supplemented with 6.4 g of sustained release Beta-Alanine or placebo for a 24 week period. Every 4 weeks participants provided a muscle biopsy and performed the CCT110%. Biopsies were analyzed for muscle carnosine content and gene expression
Results
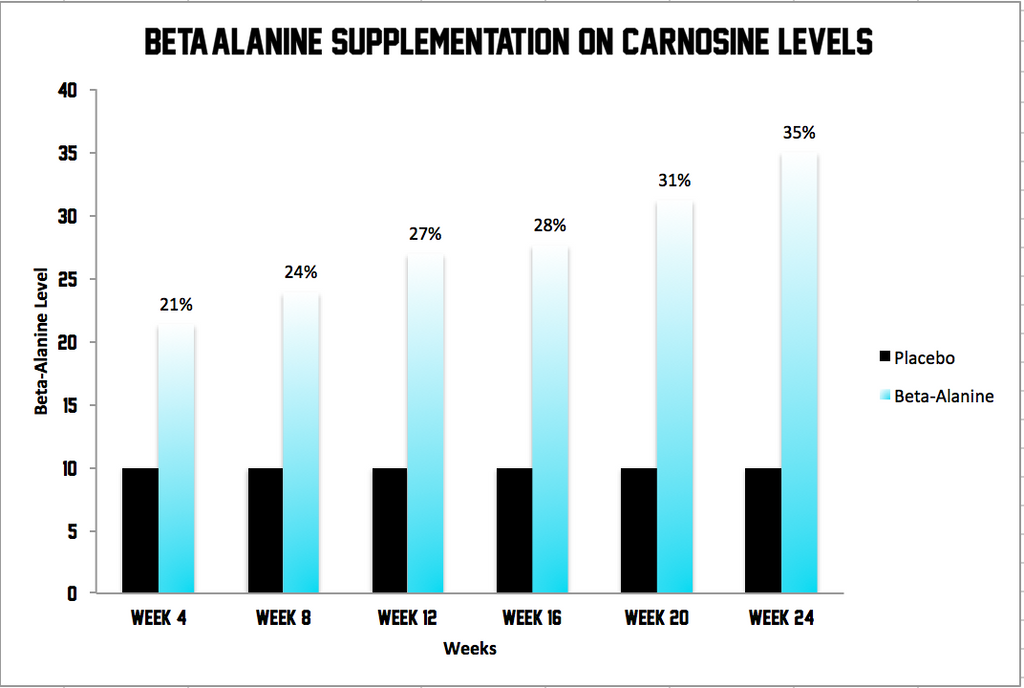
Carnosine content was increased from baseline at every time point in Beta-Alanine supplementation.
(All P < 0.0001; week 4 = +11.37 ± 7.03 mmol·kg dm, week 8 = +13.88 ± 7.84 mmol·kg dm, week 12 = +16.95 ± 8.54 mmol·kg dm, week 16 = +17.63 ± 8.42 mmol·kg dm, week 20 = +21.20 ± 7.86 mmol·kg dm, and week 24 = +20.15 ± 7.63 mmol·kg dm) but not placebo (all P > 0.05).
Conclusions
Twenty-four weeks of BA supplementation increased muscle carnosine content and improved high-intensity cycling capacity.