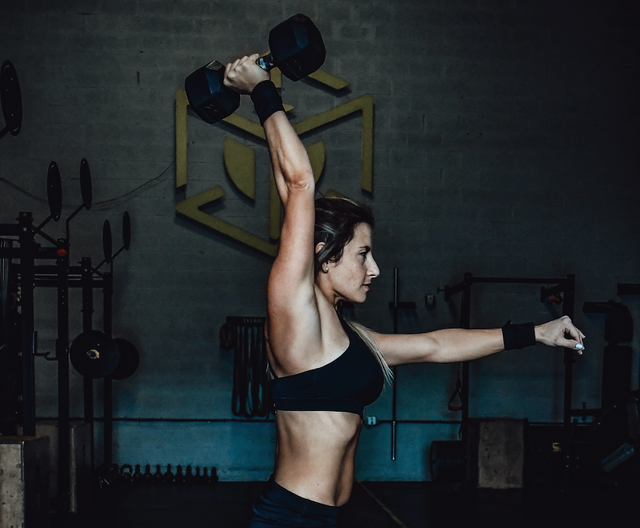
If you’re looking to build stronger, more explosive shoulders while improving balance, control, and coordination, the single-arm dumbbell push press deserves a spot in your training routine. Unlike traditional bilateral pressing movements, this dynamic exercise uses leg drive to generate upward momentum and power a dumbbell overhead — all while loading only one side of the body at a time.
The result? You build upper-body strength, lower-body coordination, and total-body athleticism — in one compact, functional movement. Whether you're a lifter chasing new overhead PRs, a CrossFitter fine-tuning your push-jerk mechanics, or an athlete looking for more power and core control, the single-arm push press delivers on all fronts.
What Is the Single-Arm Dumbbell Push Press?
The single-arm dumbbell push press is a compound, unilateral pressing movement that combines a shallow leg dip with an explosive overhead press using one arm. Unlike a strict shoulder press, it incorporates hip and knee extension to assist the lift, allowing for heavier loads, better force production, and greater muscle recruitment.
The push press enables greater load lifting compared to a strict press and enhances upper-body strength and explosive power
— Cormie et al., Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research
Muscles Worked
The movement recruits a range of muscle groups across the upper and lower body, especially when performed unilaterally.
-
Primary Movers:
-
Deltoids (anterior and medial)
-
Triceps
-
Upper Pectorals
-
-
Secondary Support:
-
Quads and Glutes (from dip and drive)
-
Serratus Anterior
-
Trapezius and Rotator Cuff
-
-
Stabilizers:
-
Core (Obliques, Rectus Abdominis, Transverse Abdominis)
-
Spinal Erectors
-
Hip Stabilizers (Glute Medius)
-
Unilateral loading significantly increases core activation and motor control compared to bilateral lifts
— Behm et al., Sports Medicine
Benefits of the Single-Arm Dumbbell Push Press
1. Improves Overhead Power
The single-arm push press trains you to use leg drive to initiate movement and smoothly transfer force through your shoulders and arms. This not only builds strong deltoids but enhances athletic power, vertical pressing capability, and total-body coordination.
Triple extension (ankle, knee, and hip) combined with shoulder pressing improves rate of force development
— Suchomel et al., Strength and Conditioning Journal
2. Targets Unilateral Strength and Stability
Unilateral pressing corrects imbalances between dominant and non-dominant sides, helping prevent shoulder injuries and muscle asymmetries. Since only one arm is loaded, your obliques, hips, and spinal stabilizers are forced to stay engaged throughout the movement.
Single-arm training improves inter-limb coordination and increases core muscle recruitment due to asymmetric load
— McCurdy et al., Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research
3. Enhances Core Strength and Anti-Rotation Control
The off-balance load challenges your body’s ability to resist rotation. This is known as anti-rotational core training, which strengthens deep trunk musculature in ways that crunches and planks can’t replicate.
Anti-rotational forces stimulate greater activation in the transverse abdominis and internal obliques
— Ekstrom et al., Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy
4. Boosts Functional Athletic Performance
The push press mimics sport-specific movement patterns like throwing, swinging, jumping, and sprinting. By integrating full-body movement and unilateral force output, it improves kinetic chain coordination — crucial for performance athletes.
5. Scalable for Strength, Hypertrophy, or Conditioning
Whether you go heavy for low reps or light for conditioning sets, this lift fits in every phase of training. It’s an excellent tool for metcons, superset finishers, or as an accessory movement for developing strength carryover to jerks and snatches.
How To Do the Single-Arm Dumbbell Push Press
-
Starting Position
-
Stand tall with feet shoulder-width apart.
-
Hold a dumbbell at shoulder level with your elbow slightly in front of the torso, palm facing inward.
-
Brace your core and keep your non-working hand on your hip or out for balance.
-
-
Dip
-
Perform a short dip by bending your knees and hips slightly (2–4 inches).
-
Keep your torso upright and heels planted.
-
-
Drive and Press
-
Explosively extend your hips and knees, transferring force upward.
-
As you rise, press the dumbbell straight overhead in one fluid motion.
-
Finish with a locked-out elbow, dumbbell over your shoulder, and a tight core.
-
-
Reset
-
Lower the dumbbell under control to shoulder height.
-
Re-brace and repeat for the desired number of reps before switching sides.
-
Proper timing of the dip and drive phase is crucial for transferring maximum force and achieving overhead lockout
— Lake et al., Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research
Programming the Push Press
Depending on your training goals, here’s how you might program this lift:
| Goal | Sets | Reps | Load |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength & Power | 4–5 | 3–5 | Heavy (70–85% 1RM) |
| Hypertrophy | 3–4 | 8–10 | Moderate (65–75% 1RM) |
| Conditioning | 3–5 Rounds | 10–12/arm | Light to Moderate |
Pair the push press with movements like goblet squats, pull-ups, or kettlebell swings for a powerful upper-lower combo circuit.
Final Thoughts on the Single-Arm Dumbbell Push Press
The single-arm dumbbell push press isn’t just a shoulder builder — it’s a full-body powerhouse. From developing explosive overhead strength and fixing left-to-right imbalances to training your core for real-world function, this unilateral movement belongs in any serious strength or athletic program.
Add it to your routine for variety, challenge, and results that go beyond just muscle. Whether you’re a beginner refining your mechanics or an advanced athlete chasing efficiency, the single-arm push press helps you press stronger, move better, and train smarter.