Beneficial effects of Apple Cider Vinegar on weight management, Visceral Adiposity Index and lipid profile in overweight or obese subjects receiving restricted calorie diet: A randomized clinical trial
Author Information
Solaleh Sadat Khezri Atoosa Saidpour Nima Hosseinzadeh Zohreh Amiri
Faculty of Nutrition and Food Technology, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Islamic Republic of Iran
Department of Clinical Nutrition & Dietetics, Faculty of Nutrition and Food Technology, National Nutrition and Food Technology Research Institute, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Islamic Republic of Iran
Faculty of Biostatistics, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Islamic Republic of Iran
Background
A randomized, clinical trial was performed to examine whether Apple cider vinegar (ACV) can result in dietary modifications that provides beneficial effects on the management of body weight and serum metabolic profiles in overweight or obese individuals.
Methods
39 study participants were randomly allocated into the ACV group (subjected to a restricted-calorie diet (RCD) with 250 kcal/day energy deficit and 30 mL/d of ACV)) or the control group (RCD only) for 12 weeks.
Results
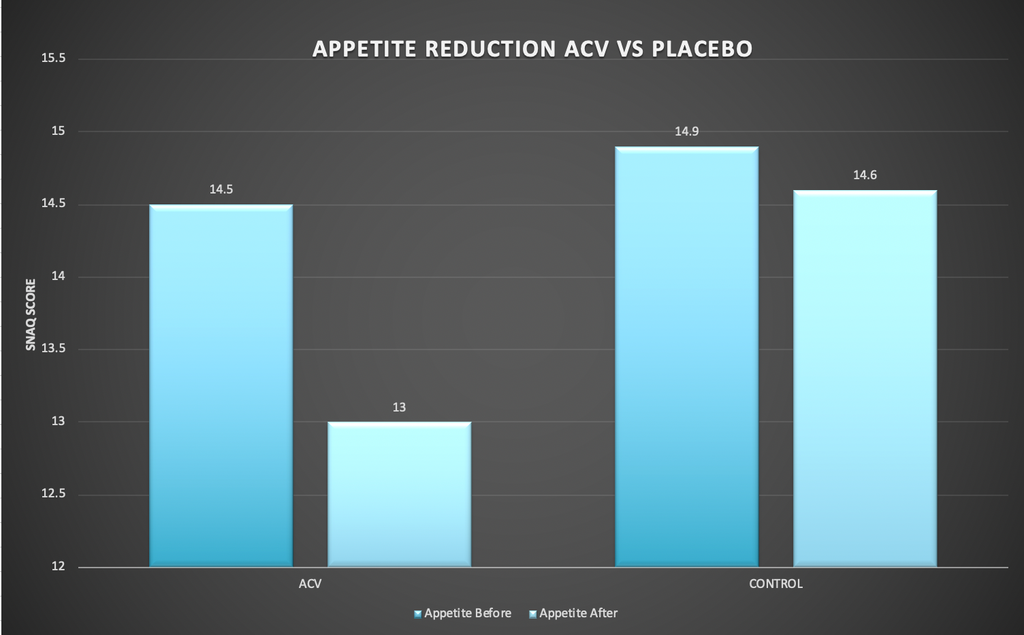
The ACV significantly reduced body weight, BMI, Hip circumference, visceral adiposity index (VAI) and appetite score (P ≤ 0.00). Furthermore, Plasma triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC) levels significantly decreased and high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) concentration significantly increased in the ACV group in comparison to the control group (P ≤ 0.05)
- Co-administration of apple cidervinegar (ACV) and restricted calorie diet (RCD) decrease body weight and BMI.
- Co-administration of ACV and RCD decrease hip circumferenceand VAI.
- Co-administration of ACV and RCD reduced plasma triglycerideconcentration and also increase in HDL-c level.
- Co-administration of ACV and RCD has a beneficial effect on appetite reduction.
Conclusions
This, ACV along with RCD can be considered as an effective strategy for reducing anthropometric parameters, TG and TC level, VAI, appetite and increasing HDL-C concentration in overweight or obese individuals.